Chapter 17 - Respiratory System
The respiratory system is responsible for taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide. It can be divided functionally into two regions:
- Conducting passages - convey air to the lungs while removing debris, warming, and humidifying the air (nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles)
- Respiratory passages - where the exchange of gases between air and blood occurs (respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and alveoli)
Respiratory epithelium is a pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells that lines much of the conducting passages.
Nasal and Oral Cavities
The nasal cavities provide an extensive surface area for removing debris, warming, and humidifying the air. The nasal and oral cavities are separated by the hard and soft palate.
Epiglottis
The epiglottis is a flap located in the throat that covers the entrance to the larynx during swallowing.
Larynx
The larynx is a hollow, tubular structure at the upper end of the trachea. It is involved in breathing and producing sound. The epithelial lining varies depending upon the region of the larynx.
Trachea
The trachea (windpipe) is a fibromuscular tube supported by C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage. It extends from the larynx toward the lungs.
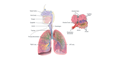
Lungs
The adult lungs are sponge-like organs. The main function of the lungs is to provide oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from blood.
Fetal Lung
The fetal lung is not capable of supporting respiration.