Chapter 16 - Urinary System
The urinary system is composed of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. Its main function is the production, storage, and expulsion of urine.
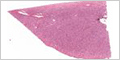
Kidney
Kidneys have several functions:
- Excretion - elimination of water-soluble metabolic wastes and foreign substances as urine
- Regulation - maintain an appropriate fluid volume and concentrations of various electrolytes in the body fluids, maintain normal blood pressure, and maintain the pH of blood
- Endocrine - secretion of hormones
- Renin - regulation of blood pressure
- Erythropoietin - stimulates production of red blood cells
- Vitamin D - regulation of calcium levels
Examine the overall structure of the kidney.
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. Each nephron includes a filter (renal corpuscle), and a single, long tubule (renal tubule) through which the filtrate passes before emerging as urine.
Each nephron is supported by a thin layer of connective tissue.
Urine is unchanged after it leaves the kidney.
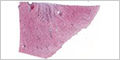
Fetal Kidney
During the development of the kidney, additional renal corpuscles form in the outer cortex as the kidney grows. Those found deeper in the inner cortex are more mature.
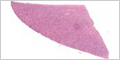
Ureter
The ureters are fibromuscular tubes that transport urine by peristalsis from the kidney to the bladder. Like the bladder, it is lined by transitional epithelium (urothelium).
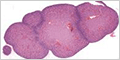
Urinary Bladder
The urinary bladder is a muscular sac that stores urine, allowing urination to be infrequent and voluntary. It is lined by transitional epithelium (urothelium), and has a thick layer of smooth muscle.