Chapter 15 - Liver and Gallbladder
The liver is an accessory digestive gland that performs over 500 distinct functions that impact all body systems.
LIVER
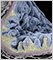
The liver is the largest internal organ of the body. The principal cell of the liver is the hepatocyte. These epithelial cells are arranged in branching plates separated by capillary sinusoids through which blood flows. The liver filters blood that comes from the digestion tract before passing it to the rest of the body.
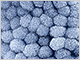
Glycogen Is the storage form of glucose found predominantly in the liver and muscle cells. Glycogen granules are composed of highly branched polymers of glucose (a type of polysaccharide) and proteins involved in their metabolism.
Bile Canaliculi
Bile canaliculi are small tubular spaces between adjacent hepatocytes that collect bile secreted by the hepatocytes.
Sinusoids
Hepatocytes are separated by sinusoidal capillaries with a discontinuous endothelium with many pores (or fenestrations).
Kupffer Cell
Kupffer cells are macrophages that reside in sinusoids of the liver. They are the largest population of macrophages in the body.
Hepatic Stellate Cell
Hepatic stellate cells (or Ito cells) store vitamin A in lipid droplets.
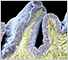
GALLBLADDER
The main functions of the gallbladder are storage, concentration, and release of bile. When released into the small intestine, bile helps break down and the absorption of fats, cholesterol, and some vitamins.
Reabsorption
The appearance of the simple columnar epithelium changes when sodium ions and water are being transported across the epithelium to concentrate bile.