Chapter 6 - Nerve Tissue
The nervous system, one of the four basic tissue types, is a complex network that coordinates actions and transmits signals between different parts of the body.
The nervous system is divided into two main components:
- Central Nervous System (CNS) - brain and spinal cord
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) - nerves and clusters of cell bodies (ganglia) located outside the CNS
NEURON
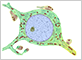
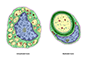
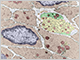
The neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are highly polarized cells with a cell body containing the nucleus, a number of branching dendrites, and a single, long axon.
Overall, the structure of neurons is optimized for receiving, processing, and transmitting information. The dendrites receive incoming signals, the cell body integrates them, and the axon transmits a signal to other neurons or cells.
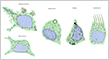
While most types of cells have similar shapes, nerve cells exhibit a wide variety of shapes.
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
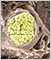
The human brain contains around 86 billion neurons organized in complex networks. The immense number of connections, often given as around 100 trillion, allows for the brain's incredible complexity and ability to process information.
Neurons
Neurons vary considerably in shape and size, but most share a common structure.
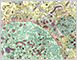
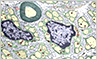
Glial Cells
Glial cells are non-neuronal cells that play vital roles in supporting and maintaining neuronal function. They outnumber neurons, although they vary by region.
There are four types of glial cells with descriptive names in the central nervous system:
- Astrocytes - provide structural and metabolic support for neurons
- Oligodendrocytes - form myelin sheaths around some axons
- Microglia - resident immune cells that resemble macrophages
- Ependymal Cells - ciliated, epithelial-like cells that line the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord
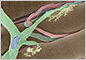
Oligodendrocytes extend processes that wrap around axons to form segments of the myelin sheaths in the central nervous system (CNS). Myelin serves as an electrical insulator, enhancing the conduction velocity of nerve fibers.
Nodes of Ranvier are small gaps between segments of the myelin sheath covering a nerve fiber.
Microglia are resident immune cells and are the least numerous of the glial cells.
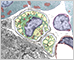
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is composed of nerves and ganglia (clusters of neuron cell bodies) that lie outside the brain and spinal cord. It connects the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body, transmitting sensory information to the CNS and motor commands to muscles and glands.
The PNS is functionally divided into two subdivisions:
- Somatic Nervous System - allows voluntary control of skeletal muscle and relays sensory information to the CNS
- Autonomic Nervous System - regulates involuntary functions, such as heart rate, digestion, and respiration
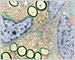
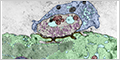
Peripheral Nerves
Peripheral nerves contain the axons of both motor neurons and sensory neurons that connect with the spinal cord. They are surrounded by multiple layers of connective tissue.
Schwann cells enclose groups of unmyelinated axons.
Myelinated axons are a portion of a neuron that is encapsulated by a fatty layer called the myelin sheath. The speed of conduction of myelinated axons is faster than unmyelinated axons.
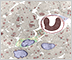
Neuromuscular Junction
A neuromuscular junction (or motor endplate) is a specialized synapse between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle cell. It transmits a signal to the muscle fiber causing its contraction.